Your Bronsted lowry acid examples images are available in this site. Bronsted lowry acid examples are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Bronsted lowry acid examples files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for bronsted lowry acid examples images information connected with to the bronsted lowry acid examples topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website always gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Bronsted Lowry Acid Examples. Bronsted - Lowry Base. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. An example of a proton acceptor is ammonia NH3. Steps for Identifying Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases.
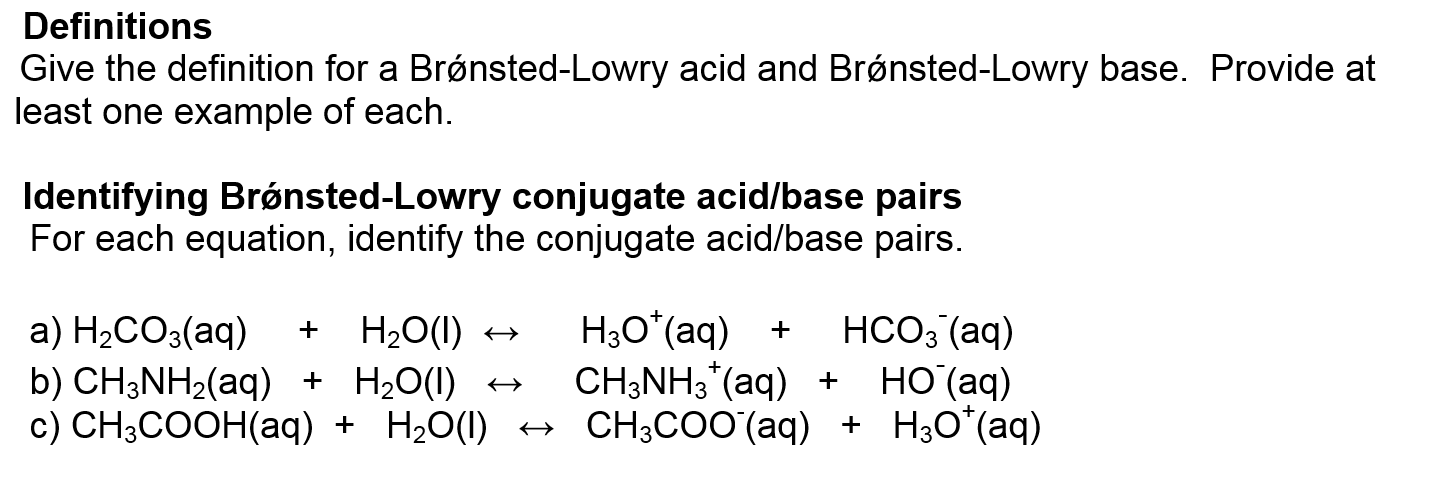 Solved Give The Definition For A Bronsted Lowry Acid And Chegg Com From chegg.com
Solved Give The Definition For A Bronsted Lowry Acid And Chegg Com From chegg.com
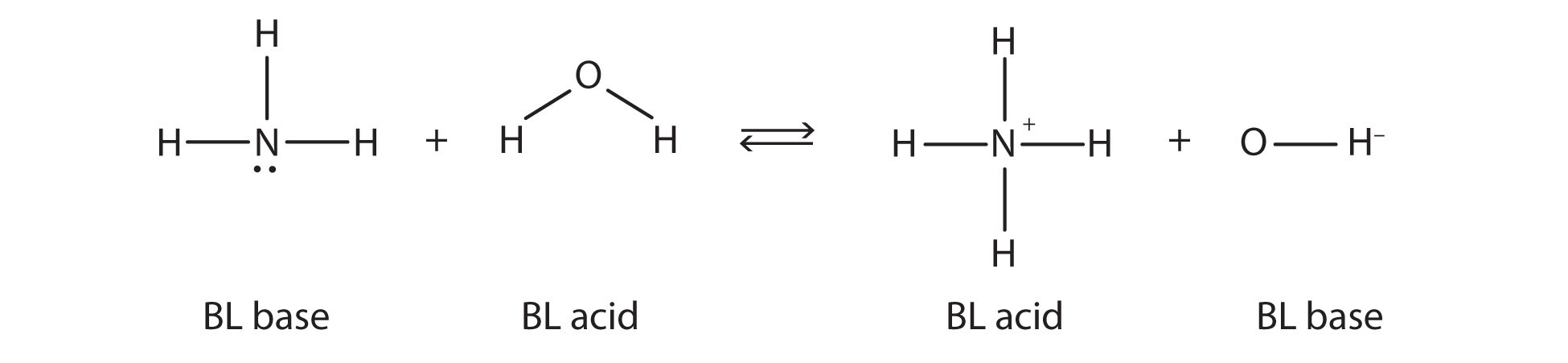
11 Is NH3 acid or base. Bronsted-Lowry Base Examples. C 6 H 5 NH 2 H 2 O C 6 H 5 NH 3 1 OH-1 2. Ammonia is the Bronsted-Lowry base because it is the proton acceptor - it accepts a hydrogen atom from water. Please refer to the example to see a Bronsted Lowry acid base pair and its conjugate pairs. In contrast a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts hydrogen ions.
Vinegar lemon juice gastric juice soft drinks examples.
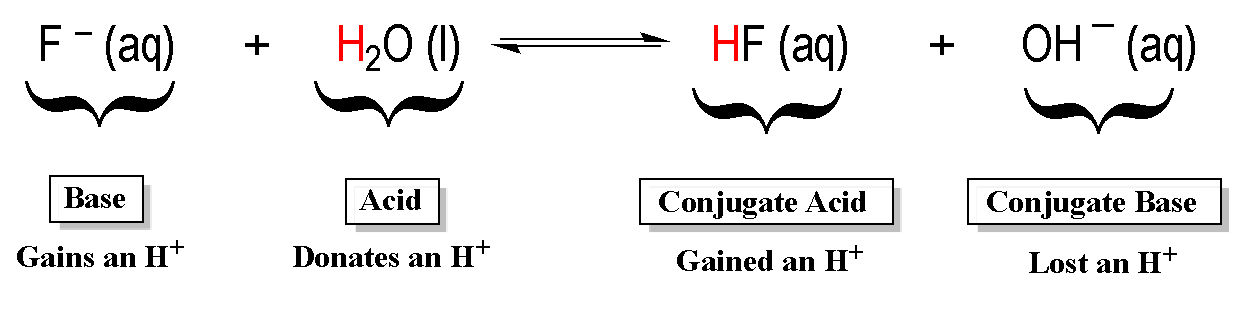
On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor. Learn the chemical characteristics of this type of acid and examples of several. On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor. In short acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. The Bronsted-Lowry acidbase definition requires a bit of analysis. The conjugate base is the hydroxide ion OH- because this is the substance produced when H2O donated the proton.
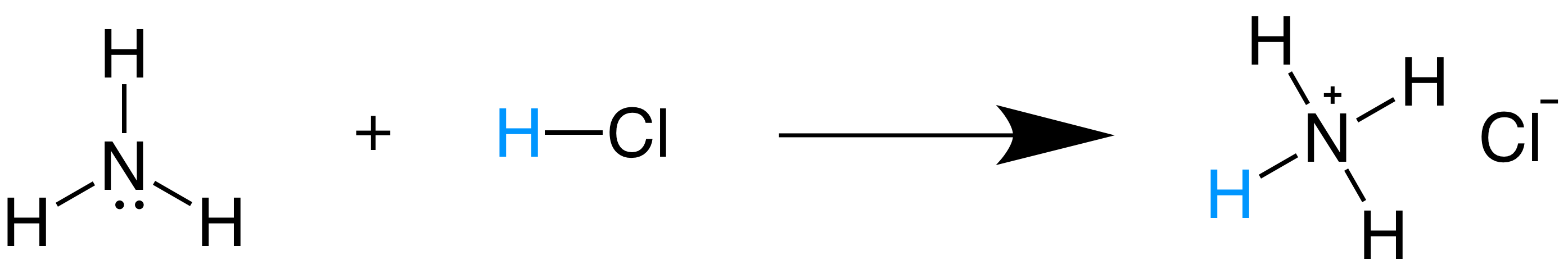 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
A Bronsted-Lowry base is a solution that is ready to accept protons in the form of hydrogen ions. All strong acids behave the same in water – 1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H 3 O ion – and very weak acids cannot act as acids in water. The two are really rather different things although there are of course many compounds that are both Lewis and Brønsted-Lowry acids ceAlOH3 for example. 14 Is a Lewis acid the same as a Brønsted base. An Arrhenius Acid is something that donates a proton to water and Bronsted-Lowry Concept extends this to any substance where an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor.
 Source: chemistrytutorials.org
Source: chemistrytutorials.org
C 6 H 5 NH 2 H 2 O C 6 H 5 NH 3 1 OH-1 2. There are many compounds that can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis base yet dont have any Brønsted-Lowry acid proton moiety. The two are really rather different things although there are of course many compounds that are both Lewis and Brønsted-Lowry acids ceAlOH3 for example. Brønsted Acids and Bases in Nonaqueous Solutions. Ammonia is the Bronsted-Lowry base because it is the proton acceptor - it accepts a hydrogen atom from water.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
According to the theory an acid and base react with each other causing the acid to form its conjugate base and the base to form its conjugate acid by exchanging a proton. HCl NH_3 rightleftharpoons NH_4 Cl- Hydrochloric acid HCl is. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. The Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory or Bronsted Lowry theory identifies strong and weak acids and bases based on whether the species accepts or donates protons or H. The Bronsted-Lowry acidbase definition requires a bit of analysis.

14 Is a Lewis acid the same as a Brønsted base. There have been different definitions proposed by different scientists. Ammonia is the Bronsted-Lowry base because it is the proton acceptor it accepts a hydrogen atom from water. The conjugate base is the hydroxide ion OH- because this is the substance produced when H2O donated the proton. Learn the chemical characteristics of this type of acid and examples of several.

12 How do you classify Bronsted acids and bases. Steps for Identifying Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases. In contrast to the acid definition a Bronsted-Lowry base is a substance that accepts protons. Substance that donates a proton. Take the following reaction for example.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases using the definitions. Substance that donates a proton. H 2 SO 4 - OH. Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases using the definitions. There have been different definitions proposed by different scientists.
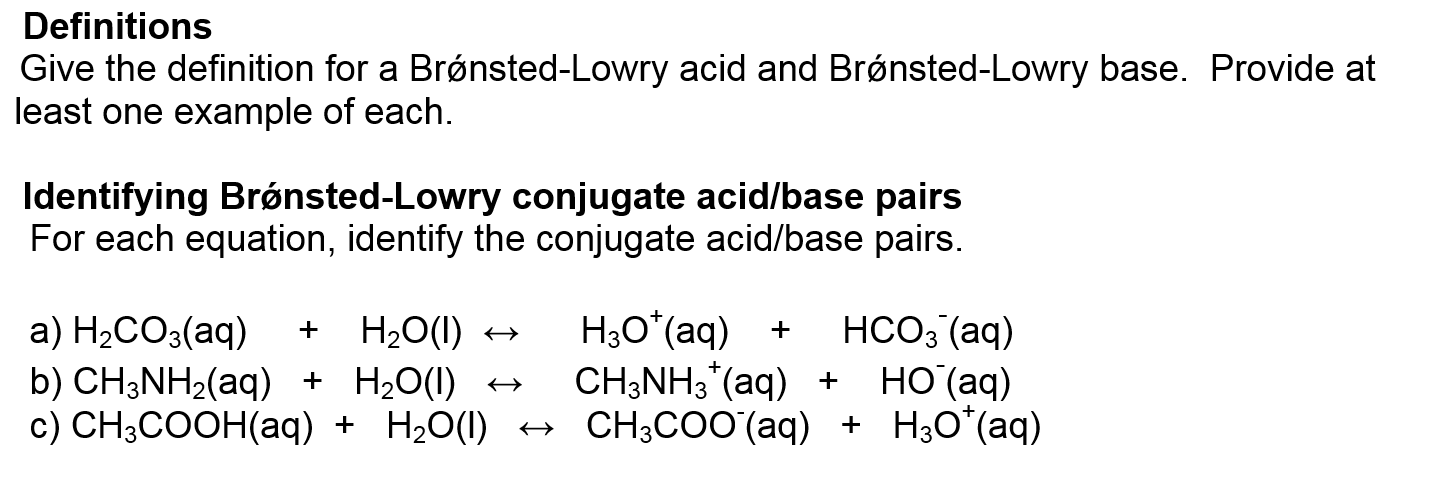 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
All strong acids behave the same in water – 1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H 3 O ion – and very weak acids cannot act as acids in water. Substance that donates a proton. Label the Bronsted-Lowry acids A bases B conjugate acids CA and conjugate bases CB in the following reactions. 16 Is ammonia a. The following Bronsted-Lowry bases list is arranged in order of decreasing base strength.
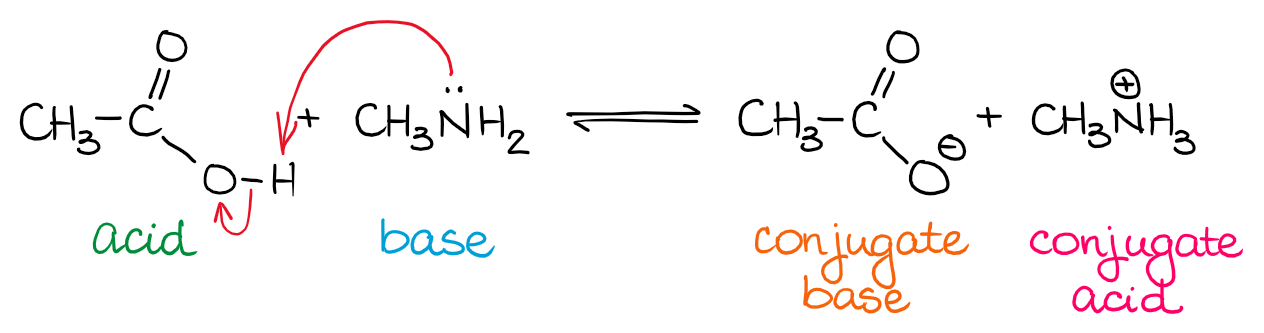 Source: organicchemistrytutor.com
Source: organicchemistrytutor.com
When it donates its proton the acid becomes its conjugate base. A conjugated acid can donate a proton and base reforms. There have been different definitions proposed by different scientists. The ammonia is happy to accept a proton from the hydrogen of water H2O to become NH4. 11 Is NH3 acid or base.
 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. The ammonia is happy to accept a proton from the hydrogen of water H2O to become NH4NH3 H2O NH4 OH-. Ammonia is the Bronsted-Lowry base because it is the proton acceptor - it accepts a hydrogen atom from water. The Bronsted-Lowry base is a substance which accepts a proton or H ion from other compounds.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A Bronsted-Lowry base is a solution that is ready to accept protons in the form of hydrogen ions. In contrast a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts hydrogen ions. In contrast to the acid definition a Bronsted-Lowry base is a substance that accepts protons. 15 How do Brønsted bases differ from Lewis bases explain with example. All strong acids behave the same in water – 1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H 3 O ion – and very weak acids cannot act as acids in water.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Bronsted-Lowry acid is a special solution that donates protons in the form of hydrogen ions due to a surplus. 11 Is NH3 acid or base. Additionally because ammonia accepted the proton from hydrochloric acid the positive ammonia ion is the conjugate acid of the equation. The following Bronsted-Lowry bases list is arranged in order of decreasing base strength. Acid-base reactions dont have to occur in water however.
 Source: jove.com
Source: jove.com
All strong acids behave the same in water – 1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H 3 O ion – and very weak acids cannot act as acids in water. A conjugated acid can donate a proton and base reforms. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. According to the theory an acid and base react with each other causing the acid to form its conjugate base and the base to form its conjugate acid by exchanging a proton. Water has a limiting effect on the strength of acids and bases.
 Source: chemistrylearner.com
Source: chemistrylearner.com
Label the Bronsted-Lowry acids A bases B conjugate acids CA and conjugate bases CB in the following reactions. Acid-base reactions dont have to occur in water however. In contrast to the acid definition a Bronsted-Lowry base is a substance that accepts protons. Take the following reaction for example. Substance that donates a proton.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
In contrast a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts hydrogen ions. Bronsted-Lowry Base Examples. Substance that donates a proton. All strong acids behave the same in water – 1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H 3 O ion – and very weak acids cannot act as acids in water. On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In contrast to the acid definition a Bronsted-Lowry base is a substance that accepts protons. Ammonia is the Bronsted-Lowry base because it is the proton acceptor - it accepts a hydrogen atom from water. When it donates its proton the acid becomes its conjugate baseA more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. Thus the products have conjugate acids and conjugate bases. On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
15 How do Brønsted bases differ from Lewis bases explain with example. 14 Is a Lewis acid the same as a Brønsted base. Vinegar lemon juice gastric juice soft drinks examples. Ammonia is the Bronsted-Lowry base because it is the proton acceptor - it accepts a hydrogen atom from water. There are many compounds that can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis base yet dont have any Brønsted-Lowry acid proton moiety.
 Source: qsstudy.com
Source: qsstudy.com
All strong acids behave the same in water – 1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H 3 O ion – and very weak acids cannot act as acids in water. Milk of magnesia bleach ammonia detergents 151 Bronsted- Lowry Acids and Bases Bronsted - Lowry Acid. In contrast a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts hydrogen ions. On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor. Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases in Water.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org
Substance that donates a proton. What is a Bronsted Lowry base example. On the other hand water is the Bronsted-Lowry acid because it is the proton donor. The conjugate base is the hydroxide ion OH- because this is the substance produced when H2O donated the proton. There have been different definitions proposed by different scientists.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title bronsted lowry acid examples by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






