Your Enzyme substrate complex example images are available in this site. Enzyme substrate complex example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Enzyme substrate complex example files here. Get all free images.
If you’re searching for enzyme substrate complex example pictures information connected with to the enzyme substrate complex example topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
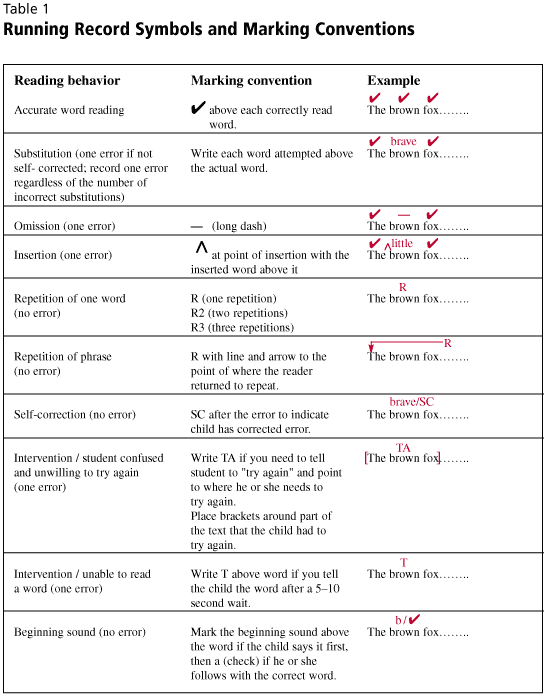
Enzyme Substrate Complex Example. The interaction of the substrate and enzyme leads to the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex. Enzymes and substrates collide to form enzyme-substrate complexes. The substrate is oriented to active place on the enzymes in such a manner that a covalent intermediate develops between the enzyme and the substrate in catalysis that occurs by covalent mechanisms. Factors affecting enzyme activity use a textbook for part a-c.
 Enzymes And Reaction Rates From www2.nau.edu
Enzymes And Reaction Rates From www2.nau.edu
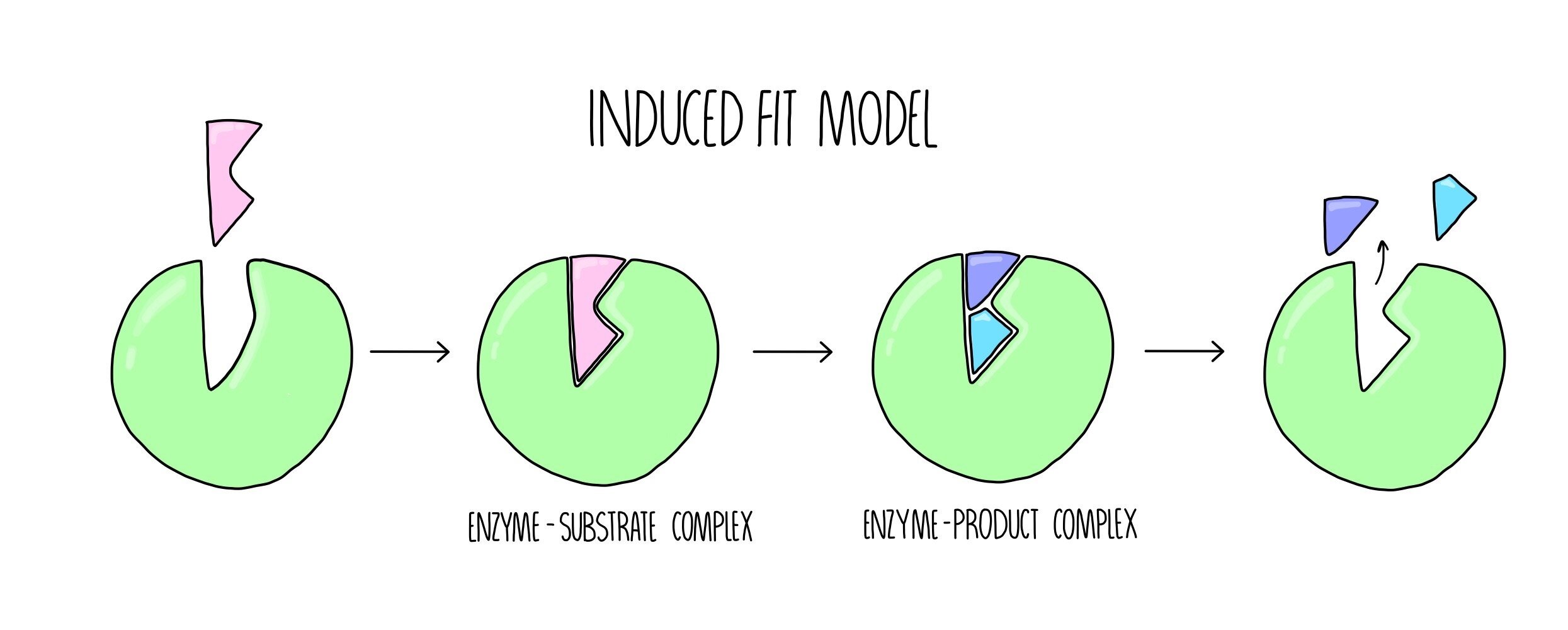
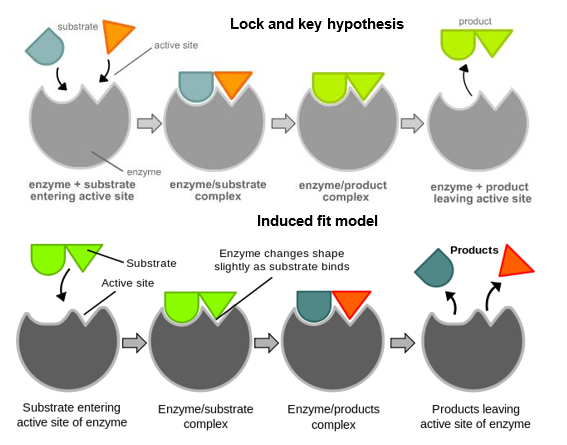
Amylase uses one substrate molecule of amylose and a cofactor of one water molecule to produce an enzyme substrate complex. The unchanged enzyme is then free to combine with other substrate molecules. The substrate is oriented to active place on the enzymes in such a manner that a covalent intermediate develops between the enzyme and the substrate in catalysis that occurs by covalent mechanisms. In this model an enzymes active site is a specific shape and only the substrate will fit into it like a lock and key. The lock and key model was first proposed in 1894. Enzymes and substrates collide to form enzyme-substrate complexes.
ATake 9 tubes add identical amount of enzyme E to each tube BEach tube contains an increasing amount of substrate S starting with zero CMeasure the velocity by determining the rate of product formation DPlot these values Velocity against substrate concentration.
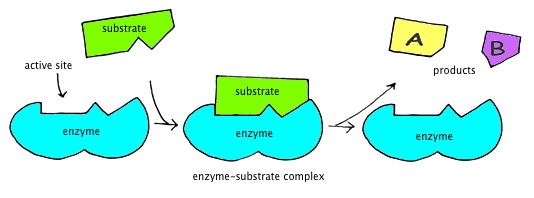
When an enzyme binds to its substrate it undergoes a conformational change or. For example the food that you eat is broken down by. The substrate is oriented to active place on the enzymes in such a manner that a covalent intermediate develops between the enzyme and the substrate in catalysis that occurs by covalent mechanisms. The unchanged enzyme is then free to combine with other substrate molecules. It is not yet clear whether a conformational change induced by the addition of substrate and. For example if we take an enzyme with an optimal pH pH opt of 70 and place it in an environment at pH 60 or 80 the charge properties of the enzyme and the substrate may be suboptimal such that binding and hence the reaction rate are lowered.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The interaction of the substrate and enzyme leads to the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex. In such a complex an enzyme requires a well-defined substrate to carry out its catalytic activities whereas numerous active spots in the enzymes bodies draw substrates to them. An enzyme will only work on one substrate - it is substrate specific. An example of how to do a kinetics experiment. The substrates are broken down or in.
 Source: alevelnotes.com
Source: alevelnotes.com
For example in the decomposition of pyruvic acid by pyruvate decarboxylase the substrate is bonded to part of a thiamine pyrophosphate molecule in the following manner. Only the enzyme-substrate complex seems to be reduced at a rate fast enough to ensure the observed hydroxylation rate 12 13. In our saliva is an enzyme amylase used to break amylose apart. Enzyme action can also be summarized by the following equation. The interaction of the substrate and enzyme leads to the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex.
 Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
If we then readjust the pH to 70 the optimal charge. ATake 9 tubes add identical amount of enzyme E to each tube BEach tube contains an increasing amount of substrate S starting with zero CMeasure the velocity by determining the rate of product formation DPlot these values Velocity against substrate concentration. The shape of the active site is complementary to its substrate like a key to its lock. For example the food that you eat is broken down by. The substrate is oriented to active place on the enzymes in such a manner that a covalent intermediate develops between the enzyme and the substrate in catalysis that occurs by covalent mechanisms.
 Source: www2.nau.edu
Source: www2.nau.edu
The lock and key model was first proposed in 1894. The affinity of substrate and enzyme is unchanged but the maximum velocity of the reaction is lessened. Temporarily binding to the substrate an enzyme can lower the energy needed for a reaction to occur thus making this reaction faster. The substrates are broken down or in. ATake 9 tubes add identical amount of enzyme E to each tube BEach tube contains an increasing amount of substrate S starting with zero CMeasure the velocity by determining the rate of product formation DPlot these values Velocity against substrate concentration.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
Enzymes and substrates collide to form enzyme-substrate complexes. In our saliva is an enzyme amylase used to break amylose apart. The substrate bonds to a small area of the enzyme termed the active site. Figure 82 Enzymes accelerate reactions by lowering the. Saturation happens because as substrate concentration increases more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex.

The substrate bonds to a small area of the enzyme termed the active site. When an enzyme binds to its substrate it undergoes a conformational change or. Start studying Enzyme-substrate complex. This region of the molecule has received the names of active site active center catalytic site or substrate site. When the enzyme is bonded to the substrate we call this the enzyme-substrate.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
For example if we take an enzyme with an optimal pH pH opt of 70 and place it in an environment at pH 60 or 80 the charge properties of the enzyme and the substrate may be suboptimal such that binding and hence the reaction rate are lowered. The substrate is oriented to active place on the enzymes in such a manner that a covalent intermediate develops between the enzyme and the substrate in catalysis that occurs by covalent mechanisms. In such a complex an enzyme requires a well-defined substrate to carry out its catalytic activities whereas numerous active spots in the enzymes bodies draw substrates to them. Saturation happens because as substrate concentration increases more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. Figure 82 Enzymes accelerate reactions by lowering the.
 Source: thesciencehive.co.uk
Source: thesciencehive.co.uk
This complementarity makes an enzyme specific to its substrate meaning the enzyme can only catalyse the reaction for its specific substrate. Product active site enzyme substrate enzyme-substrate complex. The substrates are broken down or in. ATake 9 tubes add identical amount of enzyme E to each tube BEach tube contains an increasing amount of substrate S starting with zero CMeasure the velocity by determining the rate of product formation DPlot these values Velocity against substrate concentration. The best example of this involves proteolysis by serine proteases that have both digestive enzymes and various enzymes of the blood clotting cascade.

In such a complex an enzyme requires a well-defined substrate to carry out its catalytic activities whereas numerous active spots in the enzymes bodies draw substrates to them. The shape of the active site is complementary to its substrate like a key to its lock. This region of the molecule has received the names of active site active center catalytic site or substrate site. An enzyme will only work on one substrate - it is substrate specific. The unchanged enzyme is then free to combine with other substrate molecules.

The breakdown of a substrate molecule by an enzyme. The formation of the enzymesubstrate complex at cytochrome P450 is the triggering event for the monooxygenation process. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. To form the ES complex the substrate is attached to a defined place on the enzyme. The breakdown of a substrate molecule by an enzyme.

The activity of an enzyme is influenced by certain aspects such as temperature pH co-factors activators and inhibitors. The substrate bonds to a small area of the enzyme termed the active site. The best example of this involves proteolysis by serine proteases that have both digestive enzymes and various enzymes of the blood clotting cascade. When the enzyme is bonded to the substrate we call this the enzyme-substrate. If we then readjust the pH to 70 the optimal charge.
 Source: mrgscience.com
Source: mrgscience.com
E S ES E P where E is the enzyme S is the substrate ES is the enzymesubstrate complex and P is the product. If we then readjust the pH to 70 the optimal charge. Amylase uses one substrate molecule of amylose and a cofactor of one water molecule to produce an enzyme substrate complex. The affinity of substrate and enzyme is unchanged but the maximum velocity of the reaction is lessened. Temporarily binding to the substrate an enzyme can lower the energy needed for a reaction to occur thus making this reaction faster.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
These effects are often reversible. The breakdown of a substrate molecule by an enzyme. Saturation happens because as substrate concentration increases more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. The formation of the enzymesubstrate complex at cytochrome P450 is the triggering event for the monooxygenation process. These effects are often reversible.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In our saliva is an enzyme amylase used to break amylose apart. The unchanged enzyme is then free to combine with other substrate molecules. It is not yet clear whether a conformational change induced by the addition of substrate and. This complementarity makes an enzyme specific to its substrate meaning the enzyme can only catalyse the reaction for its specific substrate. Figure 82 Enzymes accelerate reactions by lowering the.
 Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Saturation happens because as substrate concentration increases more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The unchanged enzyme is then free to combine with other substrate molecules. An example of how to do a kinetics experiment. Figure 82 Enzymes accelerate reactions by lowering the.
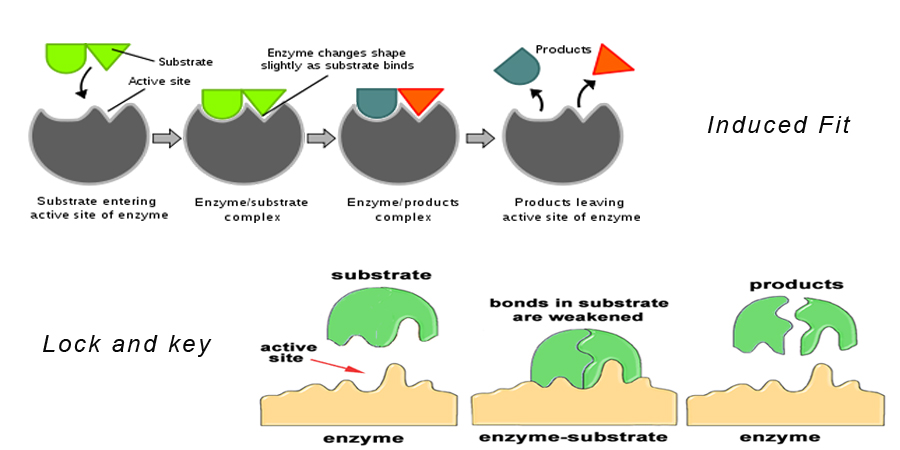 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
E S ES E P where E is the enzyme S is the substrate ES is the enzymesubstrate complex and P is the product. The lock and key model was first proposed in 1894. This region of the molecule has received the names of active site active center catalytic site or substrate site. E S ES E P where E is the enzyme S is the substrate ES is the enzymesubstrate complex and P is the product. In our saliva is an enzyme amylase used to break amylose apart.
 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
Only the enzyme-substrate complex seems to be reduced at a rate fast enough to ensure the observed hydroxylation rate 12 13. Factors affecting enzyme activity use a textbook for part a-c. The affinity of substrate and enzyme is unchanged but the maximum velocity of the reaction is lessened. When the enzyme is bonded to the substrate we call this the enzyme-substrate. Sign in to download full-size image.
 Source: botnam.com
Source: botnam.com
This is where the catalytic action of the enzyme is accomplished Fig. When the enzyme is bonded to the substrate we call this the enzyme-substrate. For example in the decomposition of pyruvic acid by pyruvate decarboxylase the substrate is bonded to part of a thiamine pyrophosphate molecule in the following manner. Factors affecting enzyme activity use a textbook for part a-c. An example of how to do a kinetics experiment.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title enzyme substrate complex example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.