Your Examples of raster data images are ready in this website. Examples of raster data are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Examples of raster data files here. Download all free images.
If you’re looking for examples of raster data pictures information linked to the examples of raster data interest, you have come to the right blog. Our website frequently provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Examples Of Raster Data. 61 Importing Raster Data. Raster Tiles This is the classical job of osm2pgsql. The Neighborhood Statistics is designed to perform several different functions on raster data involving a user defined neighborhood. Step 4 This example 1.
 Raster Data From docs.qgis.org
Raster Data From docs.qgis.org
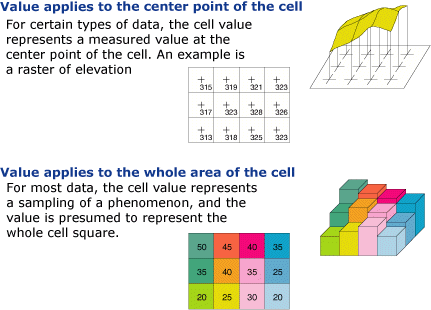
Grids added to produce raster of cells with values. For instance details concerning temperature soil PH flow elevation distance and air pressure are examples of raster data. This is a digital elevation model or DEM for part of the city of Toronto. Thematic data spectral data and pictures imagery. What is Raster Data. Figure 1215 An analysis mask b is used to clip an input raster a.
Getting raster data in is easy and can be done using the following commands.
Step 4 This example 1. What is Raster Data. Using the Raster Calculator construct an expression that multiplies each grid by its weight and adds them all creating a suitability raster. A grid of cells represents this data. The structure of spatial data explains that graphic data represented at the physical level are arranged in one of two methods for a GIS. Helper 10-24-13 20 4.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Getting raster data in is easy and can be done using the following commands. An elevation is a continuous surface that exists across the entire surface of the planet. Each pixel has an associated value. Raster data is. There are also three types of raster datasets.
 Source: edc.uri.edu
Source: edc.uri.edu
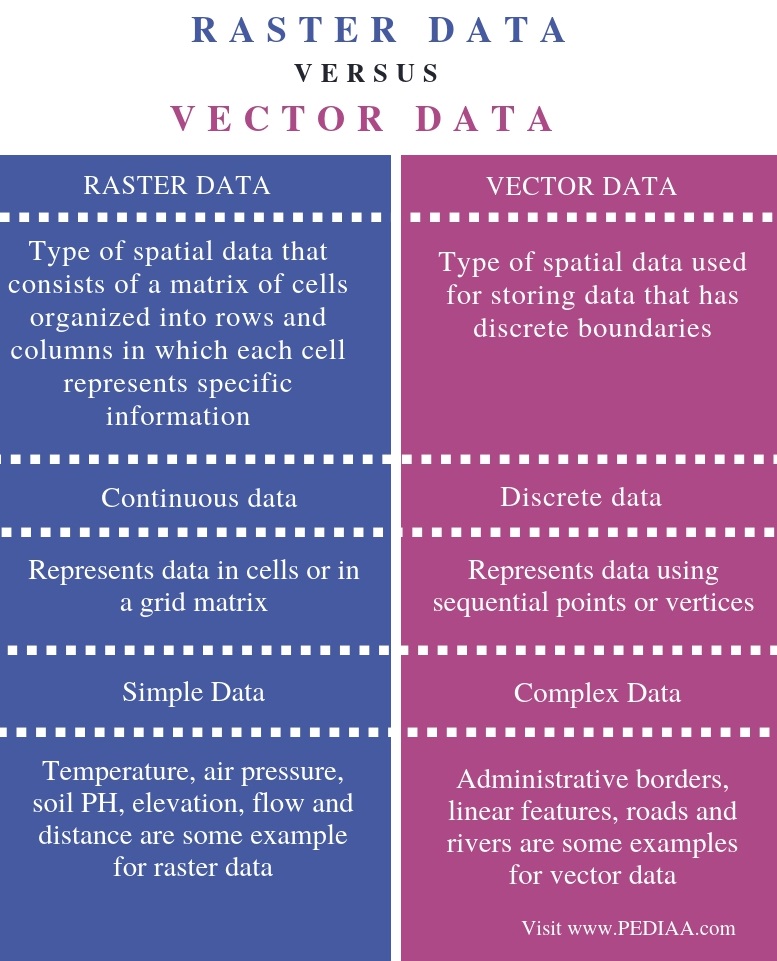
An example of discrete raster data is population density. Raster Datasets are always managed Unmanaged. In other words it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns. Chemical concentrations and elevation surface are some examples of raster data. For instance details concerning temperature soil PH flow elevation distance and air pressure are examples of raster data.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The previous chapter covered raster datasets with continuous variable where the data can take any value. This example of a thematic raster dataset is called a Digital Elevation Model DEM. In this example a dataset of land surface temperature LST measured by the MODIS sensor on board the Terra satellite is imported into R as a raster object. Raster data consists of pixels. Here we have an example of a raster data model.
 Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Raster Datasets are always managed Unmanaged. Raster Datasets are always managed Unmanaged. This chapter covers raster datasets with discrete variables where the data are classified into a limited number of values. Data set a graphic object or a query expression to create a new raster by extracting data from an existing raster. Examine classify and symbolize the new raster.
 Source: aulad.org
Source: aulad.org
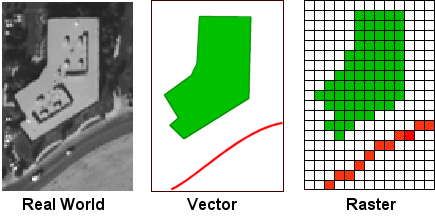
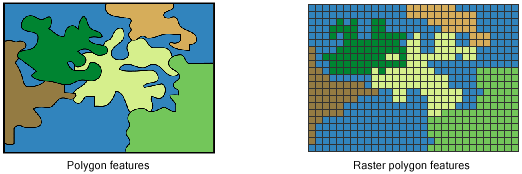
In other words it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns. So we would consider that a continuous phenomenon and thats something that lends itself well to being modeled or represented in a. Here we have an example of a raster data model. 42 Importing and plotting raster data. Most often classified raster data is continuous data and from those continuous layers we can extract the information we would need to create discrete data.
 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
For example I might start with a DEM which is a continuous expression of elevation from which I can extract slope or aspect. For instance details concerning temperature soil PH flow elevation distance and air pressure are examples of raster data. Helper 10-24-13 20 4. An example of discrete raster data is population density. 42 Importing and plotting raster data.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This is a digital elevation model or DEM for part of the city of Toronto. Raster data models consist of 2 categories discrete and continuous. 42 Importing and plotting raster data. The type of data represented in raster data is continuous while vector data is discrete. Raster and vector.
 Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Examples of vector data include rivers linear features and administrative borders. An example of discrete raster data is population density. Each pixel has an associated value. 61 Importing Raster Data. A raster object can be created by calling the raster function and specifying an external image file as an argument.
 Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Source: desktop.arcgis.com
What is Raster Data. So we would consider that a continuous phenomenon and thats something that lends itself well to being modeled or represented in a. The output raster is c which has the same area extent as the analysis mask. Raster data is. Operations for raster data generalization include Aggregate and RegionGroup.
 Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Source: desktop.arcgis.com
Each pixel has an associated value. A grid of cells represents this data. A raster object can be created by calling the raster function and specifying an external image file as an argument. An elevation is a continuous surface that exists across the entire surface of the planet. For instance details concerning temperature soil PH flow elevation distance and air pressure are examples of raster data.
 Source: gisoutlook.com
Source: gisoutlook.com
A grid of cells represents this data. Figure 1215 An analysis mask b is used to clip an input raster a. In this example a dataset of land surface temperature LST measured by the MODIS sensor on board the Terra satellite is imported into R as a raster object. Each pixel has an associated value. 42 Importing and plotting raster data.
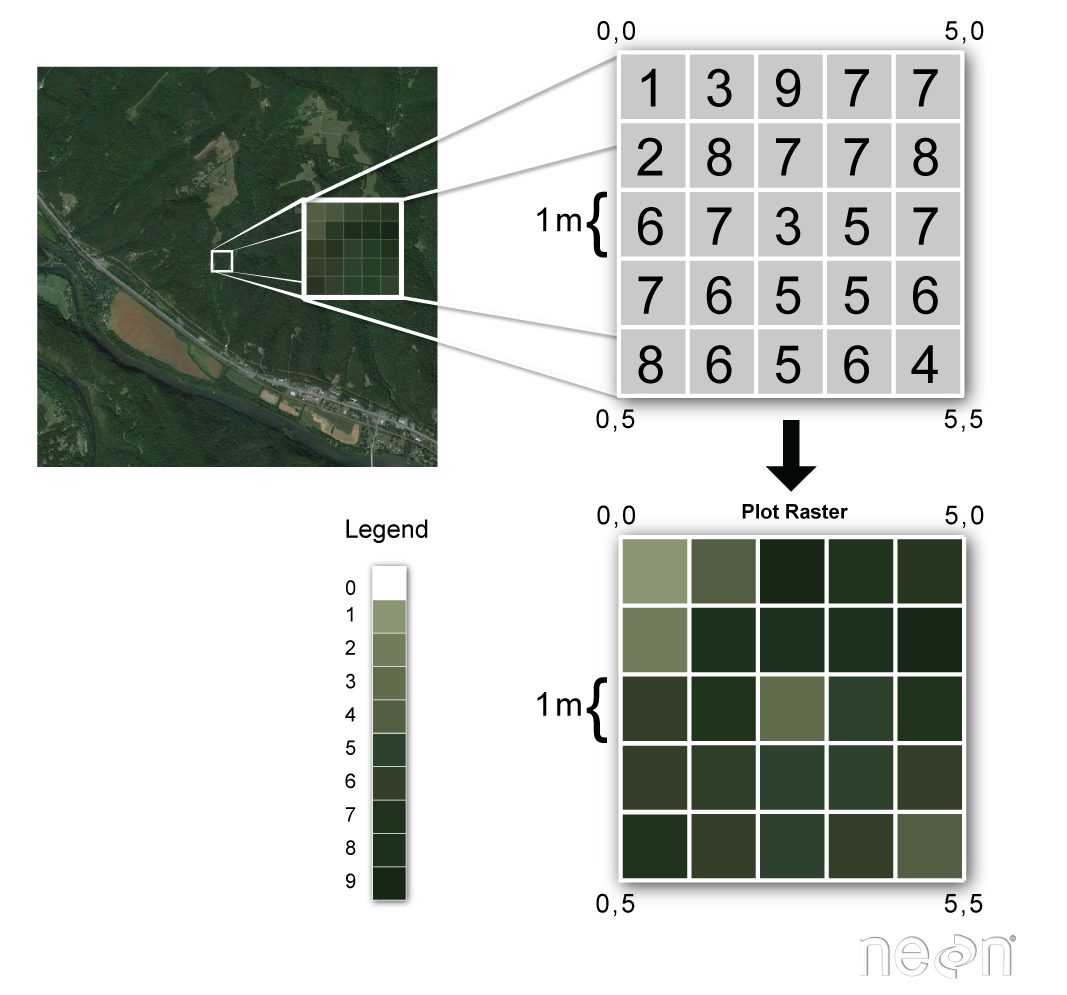 Source: datacarpentry.org
Source: datacarpentry.org
This chapter covers raster datasets with discrete variables where the data are classified into a limited number of values. 61 Importing Raster Data. Here we have an example of a raster data model. The Neighborhood Statistics is designed to perform several different functions on raster data involving a user defined neighborhood. An elevation is a continuous surface that exists across the entire surface of the planet.

61 Importing Raster Data. R1. What is raster data example. Step 4 This example 1. Here we have an example of a raster data model.
 Source: adammertel.github.io
Source: adammertel.github.io
In this example a dataset of land surface temperature LST measured by the MODIS sensor on board the Terra satellite is imported into R as a raster object. In other words it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns. Moreover lets say you are interested in calculating the average of a 9x9 rectangular neighborhood of elevations. An elevation is a continuous surface that exists across the entire surface of the planet. Import data into a database then use Mapnik or another rendering engine to create raster tiles from the data.
 Source: docs.qgis.org
Source: docs.qgis.org
Examine classify and symbolize the new raster. The output raster is c which has the same area extent as the analysis mask. Each cell has a value that represents information. Raster data consists of pixels. Examples of vector data include rivers linear features and administrative borders.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The Neighborhood Statistics is designed to perform several different functions on raster data involving a user defined neighborhood. What is Raster Data. Getting raster data in is easy and can be done using the following commands. Raster data is. This example of a thematic raster dataset is called a Digital Elevation Model DEM.
 Source: planet.uwc.ac.za
Source: planet.uwc.ac.za
Raster and vector. No valid basis for doing so. This chapter covers raster datasets with discrete variables where the data are classified into a limited number of values. This is a digital elevation model or DEM for part of the city of Toronto. 42 Importing and plotting raster data.
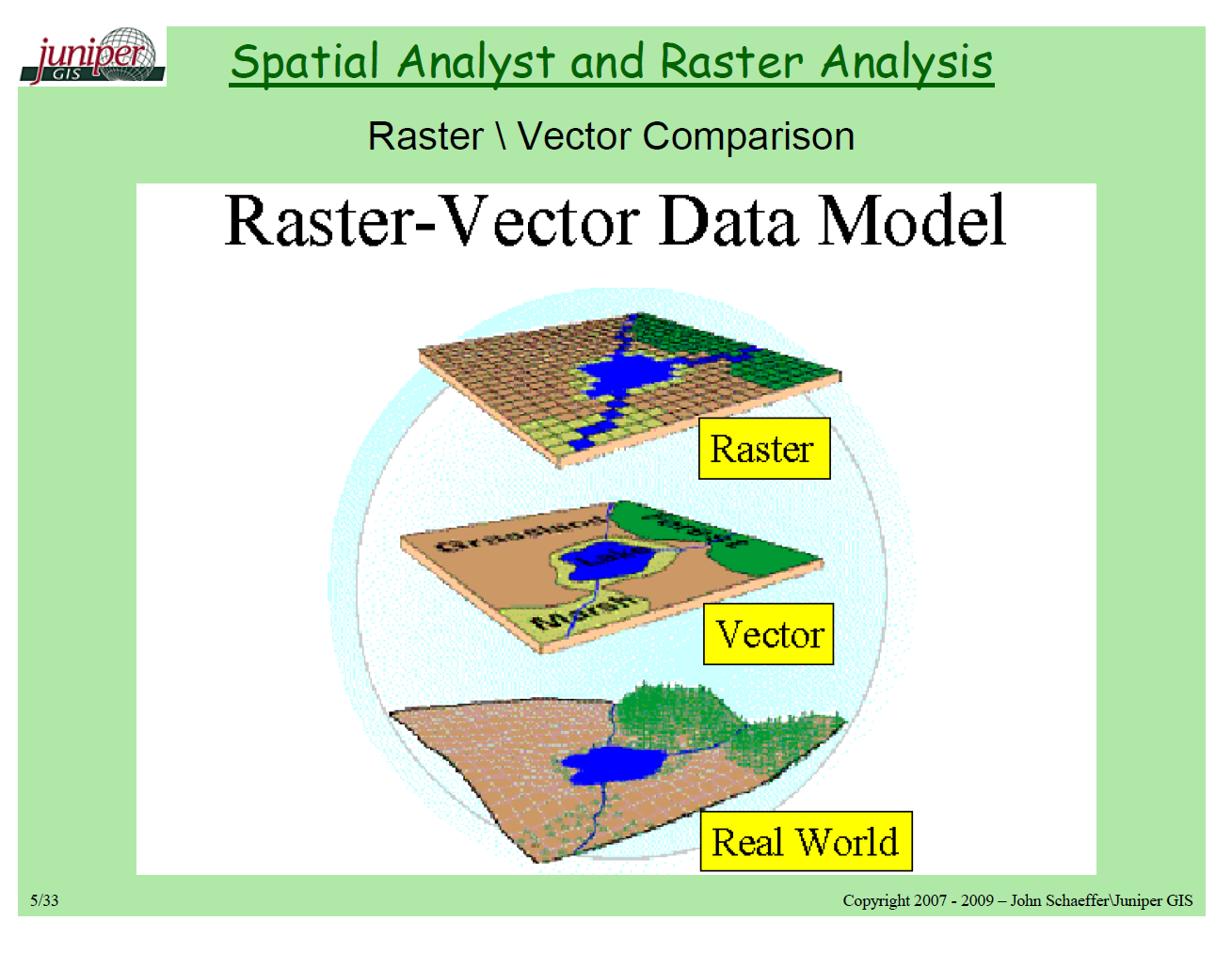 Source: newdesignfile.com
Source: newdesignfile.com
Import data into a database then use Mapnik or another rendering engine to create raster tiles from the data. Import data into a database then use Mapnik or another rendering engine to create raster tiles from the data. Raster Datasets are always managed Unmanaged. So we would consider that a continuous phenomenon and thats something that lends itself well to being modeled or represented in a. Continuous data examples are temperature and elevation measurements.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title examples of raster data by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






