Your Residual sum of squares example images are ready. Residual sum of squares example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Residual sum of squares example files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for residual sum of squares example images information related to the residual sum of squares example topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Residual Sum Of Squares Example. Residual sum of squares also known as the sum of squared errors of prediction The residual sum of squares essentially measures the variation of modeling errors. Whether to calculate the intercept for this model. Please note that this function and the following R code is partly based on a tutorial that I found here. Ordinary least squares Linear Regression.
 Sum Of Squares Residual Sum Total Sum Explained Sum Within Statistics How To From statisticshowto.com
Sum Of Squares Residual Sum Total Sum Explained Sum Within Statistics How To From statisticshowto.com
1 that minimize the residual sum of squares Sβ. For example instead of y βx one could try. LinearRegression fits a linear model with coefficients w w1 wp to minimize the residual sum of squares between the observed targets in the dataset and the targets predicted by the linear approximation. In statistics the residual sum of squares RSS also known as the sum of squared residuals SSR or the sum of squared errors of prediction SSE is the sum of the squares of residuals deviations of predicted from actual empirical values of data. Residuals in NIPALS PLS X-block residuals are calculated from TX k X T k P k In the column space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the scores T In the row space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the loadings P In Bidiag the residuals of. In other words it depicts how the variation in the dependent variable in a regression model cannot be explained by the model.
For example instead of y βx one could try.
It is calculated as. The value estimated by the regression line. Residual sum of squares Σe i 2. LinearRegression fits a linear model with coefficients w w1 wp to minimize the residual sum of squares between the observed targets in the dataset and the targets predicted by the linear approximation. By dividing the factor-level mean square by the residual mean square we obtain an F 0 value of 486 which is greater than the cut-off value of 287 from the F distribution with 4 and 20 degrees of freedom and a significance level of 005. In other words it depicts how the variation in the dependent variable in a regression model cannot be explained by the model.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
It there is some variation in the modelled values to the total sum of squares then that explained sum of squares formula is used. LinearRegression fits a linear model with coefficients w w1 wp to minimize the residual sum of squares between the observed targets in the dataset and the targets predicted by the linear approximation. The deviance calculation is a generalization of residual sum of squares. In this Example Ill explain how to use the optim function to minimize the residual sum of squares in the R programming language. The discrepancy is quantified in terms of the sum of squares of the residuals.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
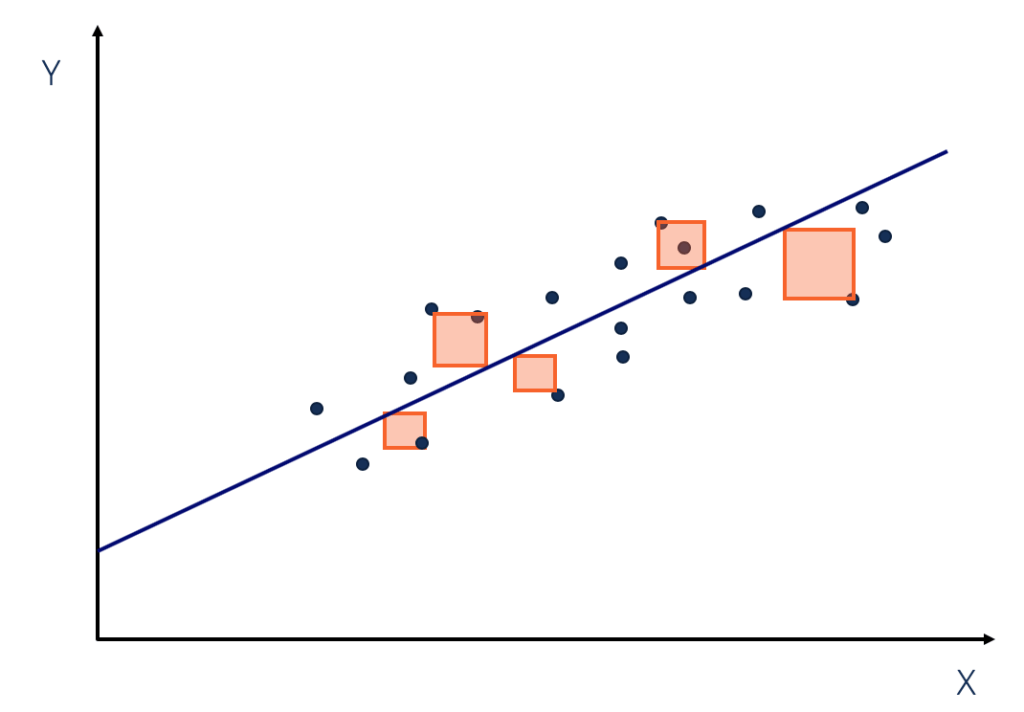
1 that minimize the residual sum of squares Sβ. The value estimated by the regression line. By comparing the regression sum of squares to the total sum of squares you determine the proportion of the total variation that is explained by the regression model R 2 the coefficient of determination. One way to understand how well a regression model fits a dataset is to calculate the residual sum of squares which is calculated as. A residual is the difference between an observed value and a predicted value in a regression model.
 Source: statology.org
Source: statology.org
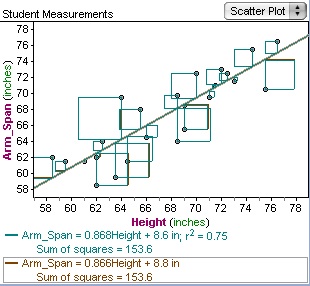
The larger this value is the better the relationship explaining sales as a function of advertising budget. 1 that minimize the residual sum of squares Sβ. Statistics - Residual Sum of Squares. There are other types of sum of squares. Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel.
 Source: mpl.loesungsfabrik.de
Source: mpl.loesungsfabrik.de
Residual sum of squares also known as the sum of squared errors of prediction The residual sum of squares essentially measures the variation of modeling errors. It is calculated as. The explained sum of squares ESS is the sum of the squares of the deviations of the predicted values from the mean value of a response variable in a standard regression model for example yi a b1x1i b2x2i. For example instead of y βx one could try. One way to understand how well a regression model fits a dataset is to calculate the residual sum of squares which is calculated as.
 Source: stats.stackexchange.com
Source: stats.stackexchange.com
In other words the description of the sums of squares for a particular effect as being the difference between the residual sum of squares for a model with and without that term only applies when the model is handled by using K-1 dummy or effect coded variables to represent the K levels of a given factor. By dividing the factor-level mean square by the residual mean square we obtain an F 0 value of 486 which is greater than the cut-off value of 287 from the F distribution with 4 and 20 degrees of freedom and a significance level of 005. There are other types of sum of squares. 1 that minimize the residual sum of squares Sβ. One way to understand how well a regression model fits a dataset is to calculate the residual sum of squares which is calculated as.
 Source: weibull.com
Source: weibull.com
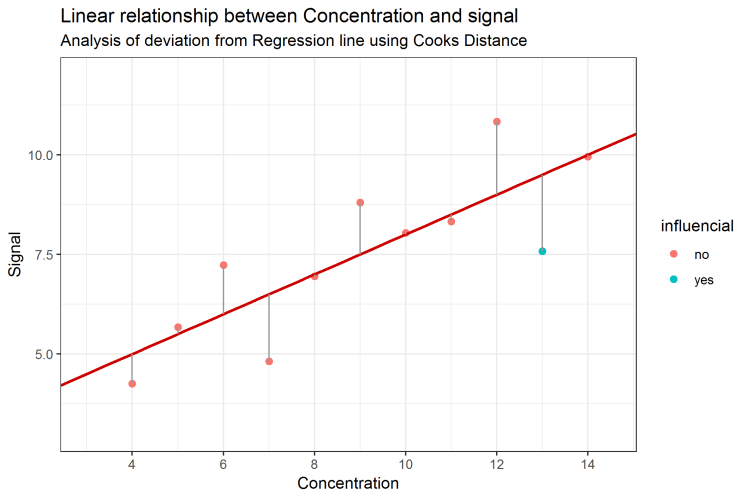
When the variance varies with x it is sometimes possible to find a transformation to correct the problem. The Residual sum of Squares RSS is defined as below and is used in the Least Square Method in order to estimate the regression coefficient. For example instead of y βx one could try. When the variance varies with x it is sometimes possible to find a transformation to correct the problem. The smallest residual sum of squares is equivalent to the largest r squared.
 Source: math.stackexchange.com
Source: math.stackexchange.com
Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel. It there is some variation in the modelled values to the total sum of squares then that explained sum of squares formula is used. Also known as the explained sum the model sum of squares or sum of squares dues to regression. 1 that minimize the residual sum of squares Sβ. The explained sum of squares ESS is the sum of the squares of the deviations of the predicted values from the mean value of a response variable in a standard regression model for example yi a b1x1i b2x2i.
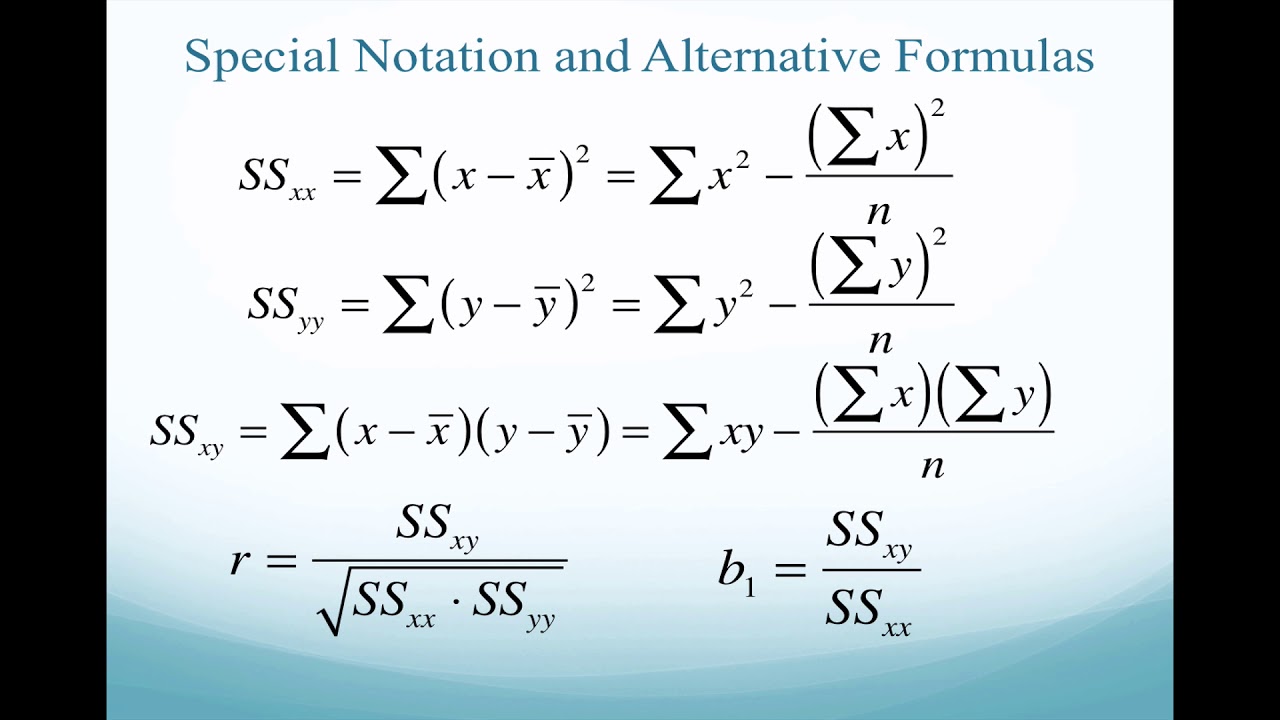 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The explained sum of squares ESS is the sum of the squares of the deviations of the predicted values from the mean value of a response variable in a standard regression model for example yi a b1x1i b2x2i. A residual is the difference between an observed value and a predicted value in a regression model. The residual sum of squares SS E is an overall measurement of the discrepancy between the data and the estimation model. When the const argument TRUE or is omitted the total sum of squares is the sum of the squared differences between the actual y-values and the average of the y-values. In other words the description of the sums of squares for a particular effect as being the difference between the residual sum of squares for a model with and without that term only applies when the model is handled by using K-1 dummy or effect coded variables to represent the K levels of a given factor.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It there is some variation in the modelled values to the total sum of squares then that explained sum of squares formula is used. A residual is the difference between an observed value and a predicted value in a regression model. When the variance varies with x it is sometimes possible to find a transformation to correct the problem. It there is some variation in the modelled values to the total sum of squares then that explained sum of squares formula is used. There are other types of sum of squares.
 Source: stats.stackexchange.com
Source: stats.stackexchange.com
Also known as the explained sum the model sum of squares or sum of squares dues to regression. For example instead of y βx one could try. Statistics - Residual Sum of Squares. The residual sum of squares SS E is an overall measurement of the discrepancy between the data and the estimation model. In statistics the residual sum of squares RSS also known as the sum of squared residuals SSR or the sum of squared errors of prediction SSE is the sum of the squares of residuals deviations of predicted from actual empirical values of data.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Residual Sum of Squares RSS is defined and given by. Instead of minimizing the residual sum of squares RSS Xn i1 y i x i 2 1 we could minimize the weighted sum of squares WSS w Xn i1 w iy i x i 2 2 This includes ordinary least squares as the special case where all the weights w i 1. There are other types of sum of squares. Residuals in NIPALS PLS X-block residuals are calculated from TX k X T k P k In the column space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the scores T In the row space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the loadings P In Bidiag the residuals of. Residual Observed value Predicted value.
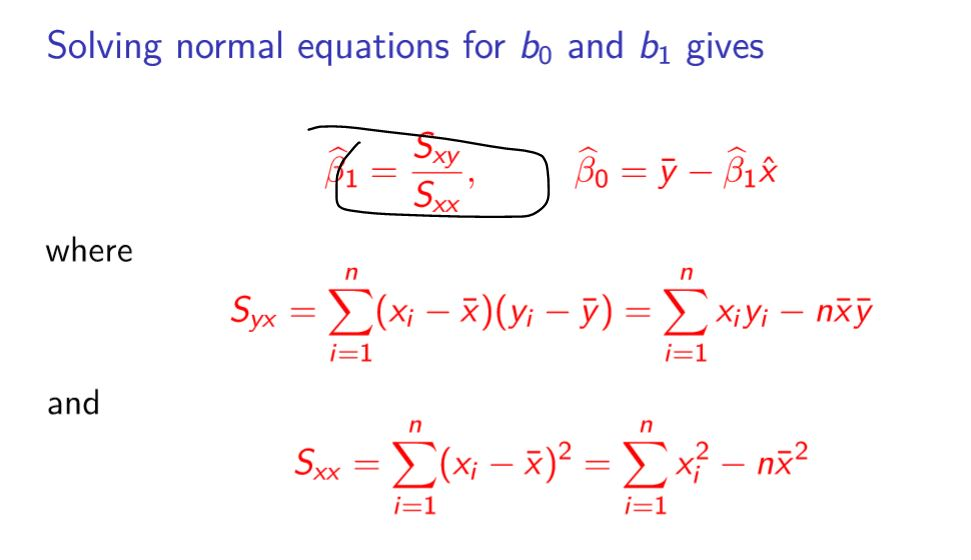 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Also known as the explained sum the model sum of squares or sum of squares dues to regression. Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel. First well manually create a function that computes the residual sum of squares. Therefore there is sufficient evidence to reject the hypothesis that the levels are all the same. The smaller the discrepancy the better the models estimations will be.
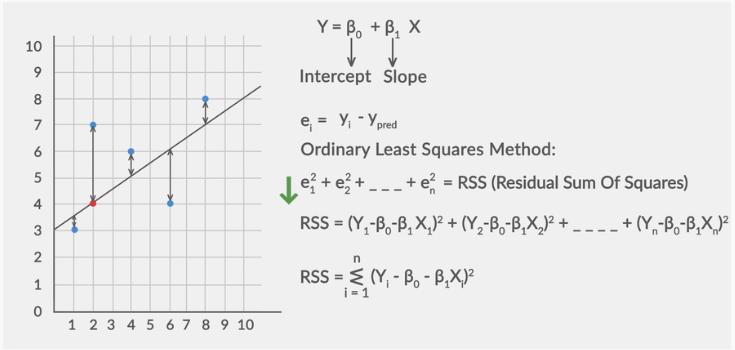 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
Residual sum of squares Σe i 2. For example if instead you are interested in the squared deviations of predicted values with respect to the average then you should use this regression sum of squares calculator. Ordinary least squares Linear Regression. The residual sum of squares for the regression model is displayed in the last cell of the second column of the output. The discrepancy is quantified in terms of the sum of squares of the residuals.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
For example if instead you are interested in the squared deviations of predicted values with respect to the average then you should use this regression sum of squares calculator. In statistics the residual sum of squares RSS also known as the sum of squared residuals SSR or the sum of squared errors of prediction SSE is the sum of the squares of residuals deviations of predicted from actual empirical values of data. Residual Sum of Squares RSS is defined and given by. First well manually create a function that computes the residual sum of squares. A residual is the difference between an observed value and a predicted value in a regression model.
 Source: statisticshowto.com
Source: statisticshowto.com
It helps to represent how well a data that has been model has been modelled. If you determine this distance for each data point square each distance and add up all of the squared distances you get. Residual Sum of Squares for Multiple Linear Regression. The distance of each fitted value y i from the no regression line y is y i y. The smaller the discrepancy the better the models estimations will be.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
One way to understand how well a regression model fits a dataset is to calculate the residual sum of squares which is calculated as. Parameters fit_intercept bool defaultTrue. When the const argument TRUE or is omitted the total sum of squares is the sum of the squared differences between the actual y-values and the average of the y-values. Do this algebra 12 Maximizing Variance Accordingly lets maximize the variance. The explained sum of squares ESS is the sum of the squares of the deviations of the predicted values from the mean value of a response variable in a standard regression model for example yi a b1x1i b2x2i.
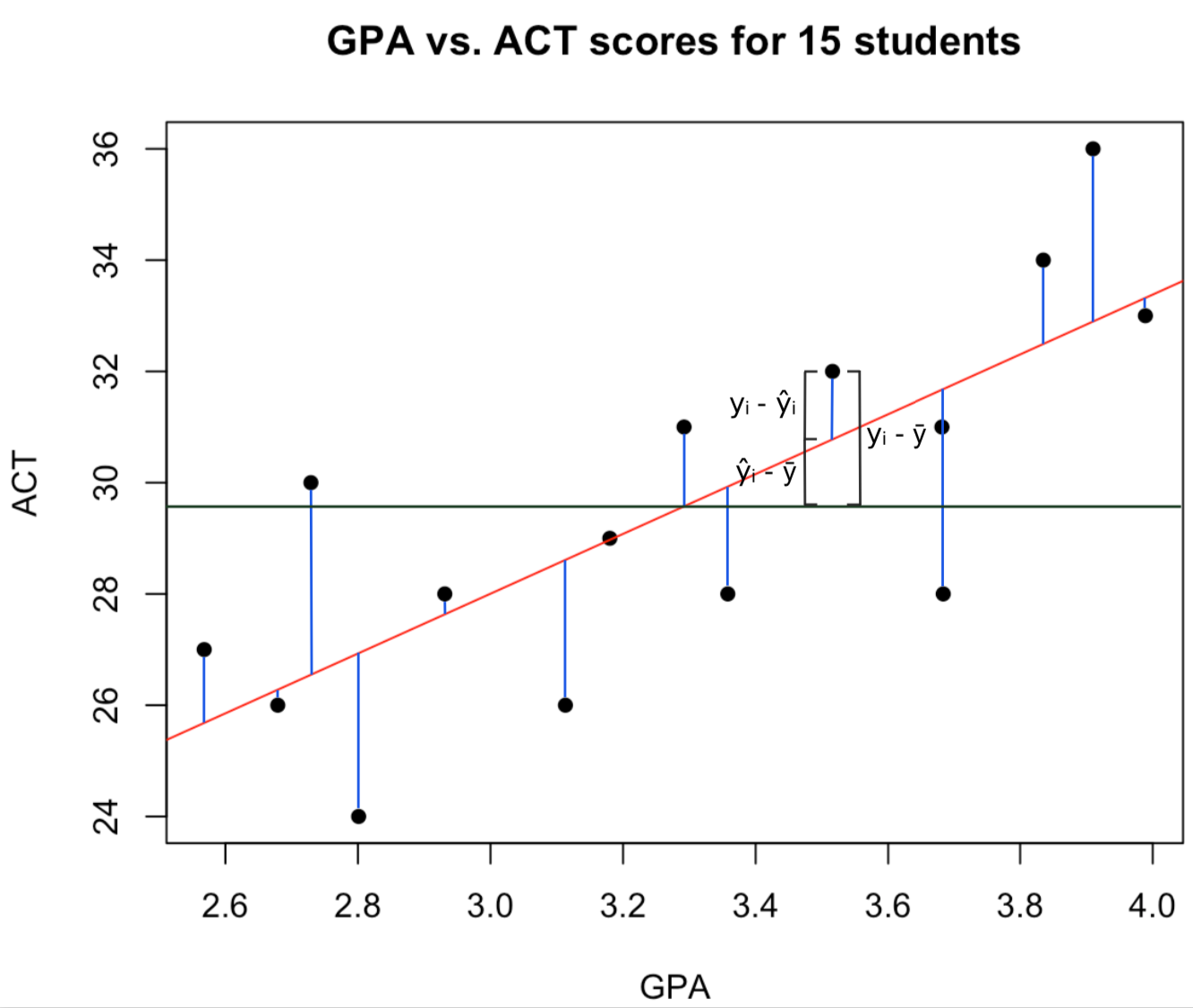 Source: towardsdatascience.com
Source: towardsdatascience.com
By dividing the factor-level mean square by the residual mean square we obtain an F 0 value of 486 which is greater than the cut-off value of 287 from the F distribution with 4 and 20 degrees of freedom and a significance level of 005. Examples for this in Chapter 14 - see Figs 1411 and 1412. Ordinary least squares Linear Regression. The value estimated by the regression line. Residuals in NIPALS PLS X-block residuals are calculated from TX k X T k P k In the column space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the scores T In the row space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the loadings P In Bidiag the residuals of.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
When the const argument TRUE or is omitted the total sum of squares is the sum of the squared differences between the actual y-values and the average of the y-values. Residuals in NIPALS PLS X-block residuals are calculated from TX k X T k P k In the column space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the scores T In the row space of X the residuals are orthogonal to the loadings P In Bidiag the residuals of. The residual sum of squares SS E is an overall measurement of the discrepancy between the data and the estimation model. When the variance varies with x it is sometimes possible to find a transformation to correct the problem. Also known as the explained sum the model sum of squares or sum of squares dues to regression.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title residual sum of squares example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.