Your Two tailed hypothesis test example images are ready. Two tailed hypothesis test example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Two tailed hypothesis test example files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for two tailed hypothesis test example images information linked to the two tailed hypothesis test example interest, you have come to the right blog. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Two Tailed Hypothesis Test Example. HOW TO Video z-test Using Excel. In this example the two-tailed p-value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference. We can perform the test at any level usually 1 5 or 10. The decision of whether to use a one or a twotailed test is important because a test statistic that falls in the region of rejection in a onetailed test may not do so in a twotailed test even though both tests use.
 When To Reject The Null Hypothesis Data Science Learning Null Hypothesis Ap Statistics From pinterest.com
When To Reject The Null Hypothesis Data Science Learning Null Hypothesis Ap Statistics From pinterest.com
μ 3 versus H A. Since the biologists test statistic t -460 is less than -16939 the biologist rejects the null hypothesis. Two-sided hypothesis test is a statistical tool to test whether the sample is greater than or less than a particular value or certain range of values. Figure 1Comparison of a a twotailed test and b a onetailed test at the same probability level 95 percent. For example suppose the null hypothesis states that the mean is equal to 10. This is a one-tailed hypothesis test o Null hypothesis.
μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are not equal H 1 left-tailed.
μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are equal The alternative hypothesis can. A two-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than or less than a certain range of values. If the sample being tested falls into either of the critical areas the alternative hypothesis is accepted instead of the null hypothesis. HOW TO Video z-test Using Excel. For a right-tailed test use the z value that corresponds to the area equivalent to 1 in Table E ie z the. The research hypothesis is that weights have increased and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Suppose it is up to you to determine if a certain state Michigan receives a significantly different amount of public school funding per student than the USA average. We will assume the sample data are as follows. With R use built-in math and statistics functions find the P-value for a two tailed hypothesis test for a mean. For example suppose the null hypothesis states that the mean is equal to 10. Set up hypotheses and determine level of significance.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In this example the two-tailed p-value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference. The decision of whether to use a one or a twotailed test is important because a test statistic that falls in the region of rejection in a onetailed test may not do so in a twotailed test even though both tests use. With R use built-in math and statistics functions find the P-value for a two tailed hypothesis test for a mean. A two-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than or less than a certain range of values. Critical area of the distribution is on both the sides or on both the tails of the region.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
N100 1971 and s256. A two-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than or less than a certain range of values. Since the biologists test statistic t -460 is less than -16939 the biologist rejects the null hypothesis. A test of a statistical hypothesis where the region of rejection is on both sides of the sampling distribution is called a twotailed test. μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are equal The alternative hypothesis can.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The decision of whether to use a one or a twotailed test is important because a test statistic that falls in the region of rejection in a onetailed test may not do so in a twotailed test even though both tests use. Suppose it is up to you to determine if a certain state Michigan receives a significantly different amount of public school funding per student than the USA average. Figure 1Comparison of a a twotailed test and b a onetailed test at the same probability level 95 percent. A two-sample t-test always uses the following null hypothesis. A paired samples t-test always uses the following null hypothesis.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A test of a statistical hypothesis where the region of rejection is on both sides of the sampling distribution is called a twotailed test. For example suppose the null hypothesis states that the mean is equal to 10. With R use built-in math and statistics functions find the P-value for a two tailed hypothesis test for a mean. The research hypothesis is that weights have increased and. Set up hypotheses and determine level of significance.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
The alternative hypothesis would be that the mean is less than 10 or greater than 10. With Python use the scipy and math libraries to calculate the P-value for a two-tailed tailed hypothesis test for a proportion. The alternative hypothesis would be that the mean is less than 10 or greater than 10. A two-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than or less than a certain range of values. Since the biologists test statistic t -460 is less than -16939 the biologist rejects the null hypothesis.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A paired samples t-test always uses the following null hypothesis. If the biologist set her significance level alpha at 005 and used the critical value approach to conduct her hypothesis test she would reject the null hypothesis if her test statistic t were less than -16939 determined using statistical software or a t-tables-3-3. The research hypothesis is that weights have increased and. For example suppose the null hypothesis states that the mean is equal to 10. Considering this when to use a one.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Since the biologists test statistic t -460 is less than -16939 the biologist rejects the null hypothesis. Considering this when to use a one. μ 3 is the probability that we would observe a test statistic less than -25 or greater than 25 if the. For a right-tailed test use the z value that corresponds to the area equivalent to 1 in Table E ie z the. Fortunately a two sample t-test allows us to answer this question.
 Source: ro.pinterest.com
Source: ro.pinterest.com
Critical area of the distribution is on both the sides or on both the tails of the region. Figure 1Comparison of a a twotailed test and b a onetailed test at the same probability level 95 percent. In this example the two-tailed p-value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference. This is a one-tailed hypothesis test o Null hypothesis. If the biologist set her significance level alpha at 005 and used the critical value approach to conduct her hypothesis test she would reject the null hypothesis if her test statistic t were less than -16939 determined using statistical software or a t-tables-3-3.
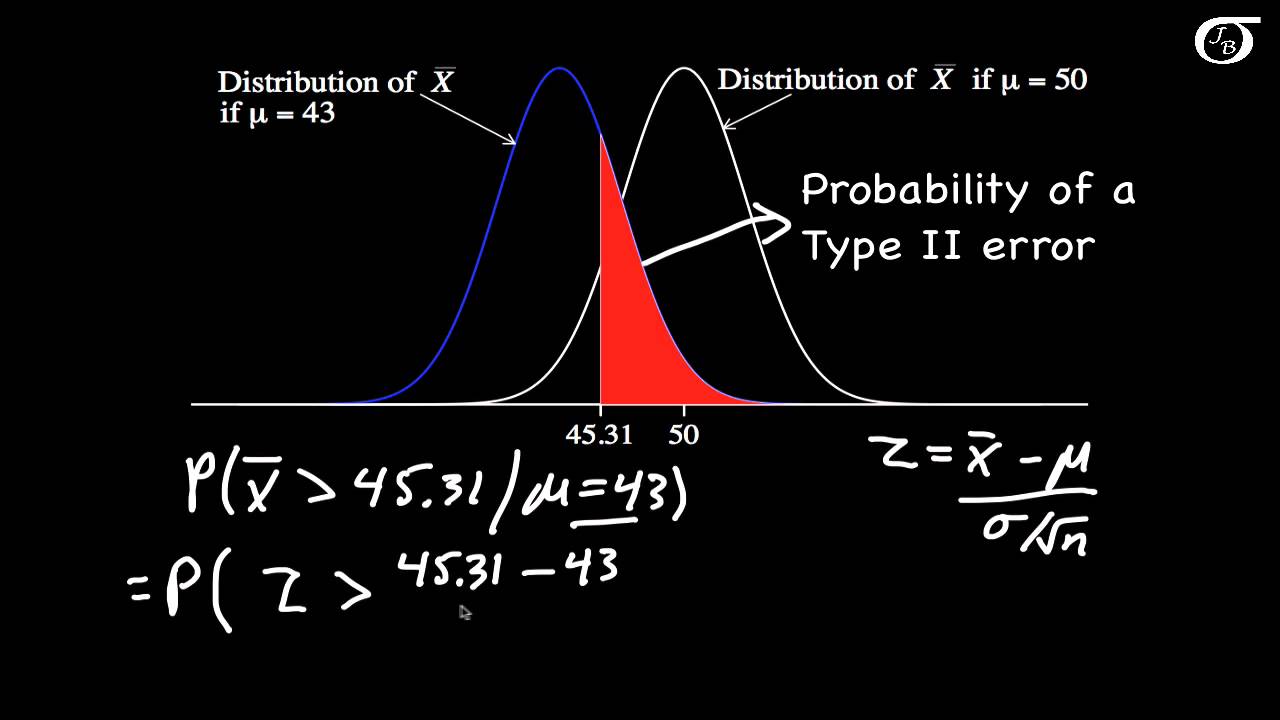 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In this example the two-tailed p-value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference. If the sample being tested falls into either of the critical areas the alternative hypothesis is accepted instead of the null hypothesis. For example suppose the null hypothesis states that the mean is equal to 10. For a right-tailed test use the z value that corresponds to the area equivalent to 1 in Table E ie z the. Suppose it is up to you to determine if a certain state Michigan receives a significantly different amount of public school funding per student than the USA average.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A paired samples t-test always uses the following null hypothesis. So depending on the direction of the one-tailed hypothesis its p-value is either 05two-tailed p-value or 1-05two-tailed p-value if the test statistic symmetrically distributed about zero. A one-tailed test looks for an increase or decrease in the parameter whereas a two-tailed test looks for any change in the parameter which can be any change- increase or decrease. Fortunately a two sample t-test allows us to answer this question. μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are equal The alternative hypothesis can.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
μ 1 μ 2 population 1 mean is less than. For a right-tailed test use the z value that corresponds to the area equivalent to 1 in Table E ie z the. Suppose it is up to you to determine if a certain state Michigan receives a significantly different amount of public school funding per student than the USA average. We will assume the sample data are as follows. A test of a statistical hypothesis where the region of rejection is on both sides of the sampling distribution is called a two-tailed test.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Hypothesis Testing Santorico - Page 286 Step 2. The research hypothesis is that weights have increased and. In this example the two-tailed p-value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference. A two-sample t-test always uses the following null hypothesis. Fortunately a two sample t-test allows us to answer this question.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The decision of whether to use a one or a twotailed test is important because a test statistic that falls in the region of rejection in a onetailed test may not do so in a twotailed test even though both tests use. HOW TO Video z-test Using Excel. A test of a statistical hypothesis where the region of rejection is on both sides of the sampling distribution is called a two-tailed test. With R use built-in math and statistics functions find the P-value for a two tailed hypothesis test for a mean. A two-tailed test also known as a non directional hypothesis is the standard test of significance to determine if there is a relationship between.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are not equal H 1 left-tailed. In this method both the sides of a critical area is used. μ 3 versus H A. The decision of whether to use a one or a twotailed test is important because a test statistic that falls in the region of rejection in a onetailed test may not do so in a twotailed test even though both tests use. Figure 1Comparison of a a twotailed test and b a onetailed test at the same probability level 95 percent.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Suppose it is up to you to determine if a certain state Michigan receives a significantly different amount of public school funding per student than the USA average. The alternative hypothesis would be that the mean is less than 10 or greater than 10. μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are equal The alternative hypothesis can. The decision of whether to use a one or a twotailed test is important because a test statistic that falls in the region of rejection in a onetailed test may not do so in a twotailed test even though both tests use. With Python use the scipy and math libraries to calculate the P-value for a two-tailed tailed hypothesis test for a proportion.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
μ 1 μ 2 the two population means are equal The alternative hypothesis can be either two-tailed left-tailed or right-tailed. For example suppose the null hypothesis states that the mean is equal to 10. A two-tailed test also known as a non directional hypothesis is the standard test of significance to determine if there is a relationship between. In this example the two-tailed p-value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference. A test of a statistical hypothesis where the region of rejection is on both sides of the sampling distribution is called a twotailed test.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Critical area of the distribution is on both the sides or on both the tails of the region. A two-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than or less than a certain range of values. Set up hypotheses and determine level of significance. Fortunately a two sample t-test allows us to answer this question. So depending on the direction of the one-tailed hypothesis its p-value is either 05two-tailed p-value or 1-05two-tailed p-value if the test statistic symmetrically distributed about zero.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title two tailed hypothesis test example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






