Your Webers law psychology example images are ready in this website. Webers law psychology example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Webers law psychology example files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for webers law psychology example images information related to the webers law psychology example interest, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website frequently provides you with hints for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Webers Law Psychology Example. Weber states that the minimum. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original. According to Webers law this difference threshold is a constant proportion of the original threshold size. Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulus.
 Cogblog A Cognitive Psychology Blog Isn T The Weber Fechner Law The Same As Any Other Equation Never Mind I Just Noticed The Difference From web.colby.edu
Cogblog A Cognitive Psychology Blog Isn T The Weber Fechner Law The Same As Any Other Equation Never Mind I Just Noticed The Difference From web.colby.edu
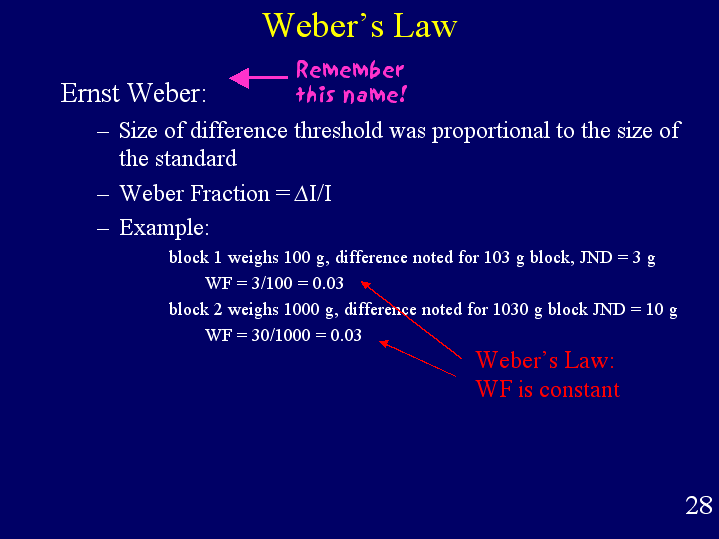
If to notice a difference the. Webers law named for German physiologist Ernst Weber is a principle of perception which states that the size of the just noticeable difference varies depending upon its relation to the strength of the original stimulus. This law was initially proposed by Ernst Heinrich Weber 1795-1878 German physician and anatomist and later elaborated to its present form by Gustav Theodor Fechner 1801-1887 already mentioned. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original stimulus. Suppose that you presented two spots of light each with an intensity of 100 units to an observer. For example imagine that you presented a sound to a participant and then slowly increased the decibel levels.
A jnd is the smallest difference between two stimuli that is detectable 50 per-cent of the time and Webers law simply means that whatever the difference between stimuli might be it is always a constant.
Basically there is actually a guy back in the day named Weber. As it stands Webers law is currently enjoying a moderate amount of experimental attention in neuropsychology. A jnd is the smallest difference between two stimuli that is detectable 50 per-cent of the time and Webers law simply means that whatever the difference between stimuli might be it is always a constant. Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulus. This law was initially proposed by Ernst Heinrich Weber 1795-1878 German physician and anatomist and later elaborated to its present form by Gustav Theodor Fechner 1801-1887 already mentioned. This includes stimuli to all senses.
 Source: cis.rit.edu
Source: cis.rit.edu
Basically there is actually a guy back in the day named Weber. This includes stimuli to all senses. Gestalt principles and ratings of physical attractiveness. WEBERS LAW Briefly stated Webers Law is a description of the just noticeable difference jnd that can be perceived by an individual. This is the currently selected item.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Neuropsychologists are trying to pin down how human neurons detect and process physical stimulation and Webers law happens to be the most long-standing theory on this phenomenon in the entire study of psychology. Each noticeable stimulus increment is a constant fraction of. This includes stimuli to all senses. Sight vision - Passage 2. The Weber-Fechner law establishes a quantitative relationship between the magnitude of a physical stimulus and how it is perceived by the subject.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
According to Webers law this difference threshold is a constant proportion of the original threshold size. In a classic example of this law the skin is touched at two separate but very close points and. 1957 Change of organization in the receptive fields of the cats retina during dark adaptation. CrossRef Google Scholar PubMed. Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulusFor example imagine that you.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
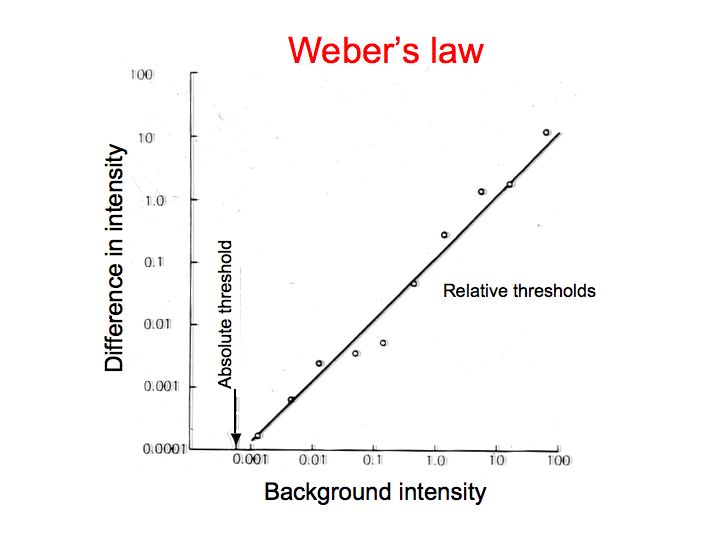
WEBERS LAW Briefly stated Webers Law is a description of the just noticeable difference jnd that can be perceived by an individual. If to notice a difference the. The size of the difference threshold a constant ratio of the standard stimulus is referred to as the Webers fraction. This law was initially proposed by Ernst Heinrich Weber 1795-1878 German physician and anatomist and later elaborated to its present form by Gustav Theodor Fechner 1801-1887 already mentioned. The mathematical representation of the beam balance model to Webers law provides for a more intuitive understand- ing of the relationship of Webers law to sensory and receptor systems.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Are you referring to Webers Law of Just Noticeable Difference Webers law also called WeberFechner law is a historically important psychological law quantifying the perception of change in a given stimulus. A jnd is the smallest difference between two stimuli that is detectable 50 per-cent of the time and Webers law simply means that whatever the difference between stimuli might be it is always a constant. Sensory adaptation and Webers Law. The WeberFechner law attempts to describe the relationship between the physical magnitudes of stimuli and the perceived intensity of the stimuliErnst Heinrich Weber 17951878 was one of the first people to approach the study of the human response to a physical stimulus in a quantitative fashion. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
It has been shown not to hold for extremes of stimulation. The size of the difference threshold a constant ratio of the standard stimulus is referred to as the Webers fraction. According to Webers law this difference threshold is a constant proportion of the original threshold size. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 30. Sensory adaptation and Webers Law.
 Source: web.colby.edu
Source: web.colby.edu
Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulusFor example imagine that you. K a constant Weber fraction In the weight example k What is Webers Law in psychology example. It has been shown not to hold for extremes of stimulation. Known as Webers law of just noticeable differences jnd or the difference thresh-old. Weber states that the minimum.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The natural relationship of the beam balance model to Webers law provides for an intuitive understanding of the relationship of Webers law to sensory and. It is a constant ratio. Weber states that the minimum. A jnd is the smallest difference between two stimuli that is detectable 50 per-cent of the time and Webers law simply means that whatever the difference between stimuli might be it is always a constant. Gestalt principles and ratings of physical attractiveness.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This is the currently selected item. Webers law is strictly obeyed by a physical beam balance as shown by the data in Table 1. For example imagine that you presented a sound to a participant and then slowly increased the decibel levels. The mathematical representation of the beam balance model to Webers law provides for a more intuitive understand- ing of the relationship of Webers law to sensory and receptor systems. This includes stimuli to all senses.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Weber noticed in 1834 that the ratio of the increment threshold the ratio of the increment threshold which is this over here to the. Weber noticed in 1834 that the ratio of the increment threshold the ratio of the increment threshold which is this over here to the. Webers law is strictly obeyed by a physical beam balance as shown by the data in Table 1. Vision hearing taste touch and smell. Webers Law states that the size of the difference threshold is proportional to the intensity of the standard stimulus.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This includes stimuli to all senses. If you are buying drinks with your friends at 5 each and there is a nicer drink that costs 10 you might hesitate to buy it because 5 extra seems like too much but if youre buying a piece of furniture for 500 and see something you like. Suppose that you presented two spots of light each with an intensity of 100 units to an observer. Weber states that the minimum. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original.
 Source: apps.usd.edu
Source: apps.usd.edu
The WeberFechner law attempts to describe the relationship between the physical magnitudes of stimuli and the perceived intensity of the stimuliErnst Heinrich Weber 17951878 was one of the first people to approach the study of the human response to a physical stimulus in a quantitative fashion. Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulusFor example imagine that you presented a sound to a participant and then slowly increased the decibel levels. Known as Webers law of just noticeable differences jnd or the difference thresh-old. As it stands Webers law is currently enjoying a moderate amount of experimental attention in neuropsychology. WEBERS LAW Briefly stated Webers Law is a description of the just noticeable difference jnd that can be perceived by an individual.
 Source: cis.rit.edu
Source: cis.rit.edu
Known as Webers law of just noticeable differences jnd or the difference thresh-old. Suppose that you presented two spots of light each with an intensity of 100 units to an observer. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original stimulus. Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulusFor example imagine that you presented a sound to a participant and then slowly increased the decibel levels. In a classic example of this law the skin is touched at two separate but very close points and.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Weber states that the minimum. Webers Law also sometimes known as the Weber-Fechner Law suggests that the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulusFor example imagine that you. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 30. Each noticeable stimulus increment is a constant fraction of. Webers law named for German physiologist Ernst Weber is a principle of perception which states that the size of the just noticeable difference varies depending upon its relation to the strength of the original stimulus.
 Source: instruct.uwo.ca
Source: instruct.uwo.ca
The mathematical representation of the beam balance model to Webers law provides for a more intuitive understand- ing of the relationship of Webers law to sensory and receptor systems. If to notice a difference the. A jnd is the smallest difference between two stimuli that is detectable 50 per-cent of the time and Webers law simply means that whatever the difference between stimuli might be it is always a constant. 1965 Optic nerve impulses and Webers Law. Neuropsychologists are trying to pin down how human neurons detect and process physical stimulation and Webers law happens to be the most long-standing theory on this phenomenon in the entire study of psychology.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
How do you use Webers law. It is a constant ratio. WEBERS LAW Briefly stated Webers Law is a description of the just noticeable difference jnd that can be perceived by an individual. How do you use Webers law. Basically there is actually a guy back in the day named Weber.
 Source: cns.nyu.edu
Source: cns.nyu.edu
How do you use Webers law. Weber states that the minimum. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original. JND k I where I Intensity of the standard stimulus. WEBERS LAW Briefly stated Webers Law is a description of the just noticeable difference jnd that can be perceived by an individual.
Each noticeable stimulus increment is a constant fraction of. Gustav Theodor Fechner 18011887 later offered an elaborate. Webers law also called Weber-Fechner law historically important psychological law quantifying the perception of change in a given stimulus. Webers Law states that the ratio of the increment threshold to the background. The law states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original stimulus.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title webers law psychology example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.